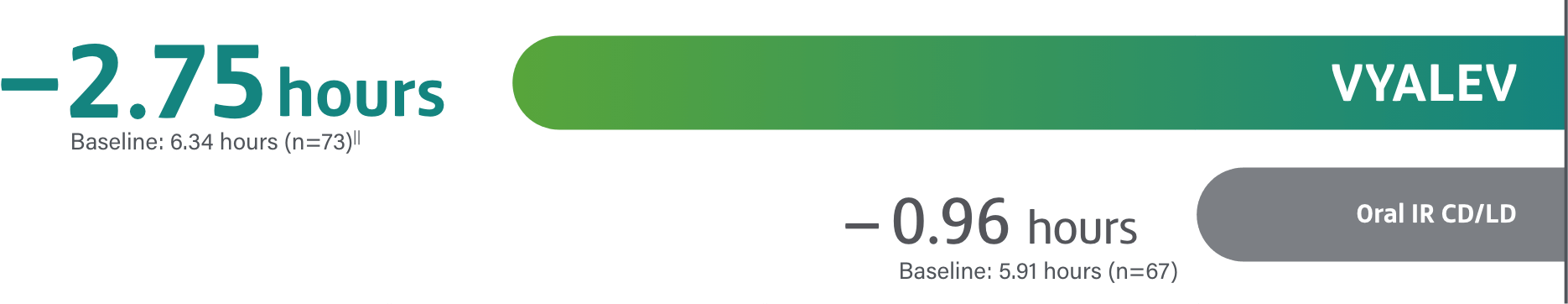Text on screen: VYALEV is indicated for the treatment of motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Before using VYALEV, it is important that you provide training to the patient at your office.
Please see Important Safety Information throughout this video, and see accompanying Full Prescribing Information, which is also available at https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/vyalev_pi.pdf.
Text on screen: Janice & Faron’s Story
Text on screen: Janice is an actual VYALEV patient and was on prescribed therapy when she provided a testimonial. Changes in therapy status may have occurred since that time.
VO (Janice): My name is Janice, and I was diagnosed with Parkinson’s in 2014 when I was 50 years old.
VO (Faron): My name’s Faron. I’m the other half.
VO (Janice): My doctor got me on the oral carbidopa/levodopa, and it did…it did
pretty well for a while. I was taking probably about 8 pills a day, at least.
VO (Faron): It was a lot of pills...
VO (Janice): You have to be careful because you can’t eat a lot of proteins with it. With VYALEV, I don’t have to worry about that.
Text on screen: VYALEV (foscarbidopa/foslevodopa) is delivered under the skin through a wearable pump and does not pass through the stomach. Food does not affect VYALEV exposure or absorption.
VO (Janice): The oral meds I was taking were good, but only, only for a certain amount of time. And I was having more highs and lows—it was like a roller-coaster.
VO (Janice): I talked to my doctor and I, I knew I needed something a little more.
VO (Faron): I think he just knew that it was time for her because it was advancing.
VO (Janice): I started VYALEV when I was 57 years old. My doctor
thought I would be an excellent candidate because of the “Off” times that
I was experiencing with my oral meds. It wasn’t a surgical procedure, and
we just felt like this was the next step.
Text on screen: Let the patient know to keep a supply of oral immediate-release carbidopa/levodopa tablets with them in case they are unable to use the VYALEV (foscarbidopa/foslevodopa) infusion.
VO (Janice): VYALEV gives me more “On” time. It can be in your system constantly. They can adjust it depending on how I’m feeling—if I feel like I’m not getting enough or if I’m getting too much.
VO (Janice): There’s different ways that you can wear it: you can wear it on a hip or you can have it going this way across your body. You know, sometimes I forget that I’m wearing it until it beeps to tell me that I need to change the battery or the, uh, medicine. It’s just, it’s not in the way.
Text on screen: Instruct your patient to refer to the full Prescribing Information, Medication Guide, and Instructions for Use that came with their drug vials, pump, and supplies from the Specialty Pharmacy.
VO (Janice): When they explained VYALEV to me, at first I thought, oh my gosh, this is a lot of steps. Once I started doing it, it didn’t seem like there was that many steps to it. Probably maybe less than 10 minutes to complete my daily routine. You know, it’s like combing your hair or brushing your teeth; it’s just another step. Plucking your eyebrows, do your pump.
VO (Janice): Parkinson’s hasn’t stopped me! It’s not defining my life. I’m kind of telling it what to do, and we work together. VYALEV has helped me.
Text on screen (with VO to match): IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATION
INDICATION
VYALEV is indicated for the treatment of motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
VYALEVTM (foscarbidopa/foslevodopa) is contraindicated in patients who are currently taking or have taken (within 2 weeks) a nonselective monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor, as concurrent use can cause hypertension.
Patients treated with levodopa (the active metabolite of VYALEV) have reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living, including the operation of motor vehicles, which sometimes resulted in accidents. Although many of these patients reported somnolence while on levodopa, some perceived that they had no warning signs, such as excessive drowsiness, and believed they were alert immediately prior to the event (sleep attack). Some of these events have been reported more than one year after initiation of treatment. For this reason, prescribers should continually assess VYALEV-treated patients for drowsiness or sleepiness. Advise patients about the potential to develop drowsiness with VYALEV and ask about factors that may increase risk of somnolence. Consider discontinuing VYALEV in patients who report significant daytime sleepiness or episodes of falling asleep during activities that require active participation. If VYALEV is continued, patients should be advised not to drive and to avoid other potentially dangerous activities that might result in harm if the patient becomes somnolent. There is insufficient information to establish that dose reduction will eliminate episodes of falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living.
There is an increased risk for hallucinations and psychosis in patients taking VYALEV. Hallucinations associated with levodopa may present shortly after the initiation of therapy and may be responsive to dose reduction of VYALEV or other concomitantly administered medications. Patients with a major psychotic disorder should not be treated with VYALEV.
Patients may experience intense urges while on VYALEV. Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is important for prescribers to ask patients or their caregivers specifically about the development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges, uncontrolled spending, binge or compulsive eating, or other urges while on VYALEV. Consider reducing the dose or discontinuing VYALEV if a patient develops such urges.
VYALEV can cause infusion site reactions and infections. Various types of reactions at the infusion site have been reported, including erythema, pain, edema, nodules, warmth, swelling, and others. The most frequent infusion site infection reported was cellulitis. If an infection is suspected at the infusion site, the cannula should be removed. In such a case, either a new cannula should be placed at a new infusion site or, in the event of a prolonged interruption, prescribe an oral carbidopa/levodopa product until the patient is able to resume VYALEV.
Withdrawal-emergent hyperpyrexia and confusion, a symptom complex that resembles neuroleptic malignant syndrome (characterized by elevated temperature, muscular rigidity, altered consciousness, and autonomic instability), with no other obvious etiology, has been reported in association with rapid dose reduction, withdrawal, or change in dopaminergic therapy. Avoid sudden discontinuation or rapid dose reduction of VYALEV.
VYALEV may cause or exacerbate dyskinesias, which may require a dose reduction of VYALEV or other medicines used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
Myocardial infarction and arrhythmia were reported in patients taking carbidopa/levodopa (the active metabolites of VYALEV). Ask patients about symptoms of ischemic heart disease and arrhythmia, especially those with a history of myocardial infarction or cardiac arrhythmias.
Monitor patients with glaucoma after starting VYALEV as it may cause increased intraocular pressure.
Drug Interactions: The use of nonselective MAO inhibitors is contraindicated. Selective MAO-B inhibitors may be associated with orthostatic hypotension. Concurrent administration with antihypertensives can cause symptomatic postural hypotension, which may require a dose adjustment of the antihypertensive. Coadministration with dopamine D2 antagonists or isoniazid may reduce the effectiveness of VYALEV.
The most common adverse reactions for VYALEV that occurred in ≥3% of patients, and at least 2% difference from oral immediate-release carbidopa/levodopa, were infusion/catheter site reactions, infusion/catheter site infections, hallucinations, dyskinesia, On and Off phenomenon, balance disorder, constipation, peripheral swelling, agitation, insomnia, psychotic disorder, and dyspnea.
VYALEV (foscarbidopa and foslevodopa) injection for subcutaneous use is available in a 120 mg foscarbidopa and 2,400 mg foslevodopa per 10 mL (12 mg foscarbidopa and 240 mg foslevodopa per mL) solution.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information or visit https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/vyalev_pi.pdf.
REFERENCES:
- VYALEV [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.
- Aldred J, Anca-Herschkovitsch M, Antonini A, et al. Application of the “5-2-1” screening criteria in advanced Parkinson’s disease: interim analysis of DUOGLOBE. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2020;10(5):309-323. doi:10.2217/nmt-2020-0021
- Boelens Keun JT, Arnoldussen IAC, Vriend C, van de Rest O. Dietary approaches to improve efficacy and control side effects of levodopa therapy in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(6):2265-2287. doi:10.1093/advances/nmab06
- VYALEV Pump Carrying Accessory Instructions for Use. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.